data_str
Introduction to Data structures and Operators in R
 Nilanjan Chatterjee
Nilanjan Chatterjee
February, 2020
Topics to be covered
- Data Structure
- What is data structure?
- Different types of data structures
- Conversion between data structures
- Operators
Data Structures in R
We all have used/ will use data for our analysis before but have you ever thought about the different type of structures to hold the data
- Why ?
- How ?
Different types of data strctures
-
What is the dimension of your data?
-
What is data composed of ?
Different types of data strctures

Different types of data strctures
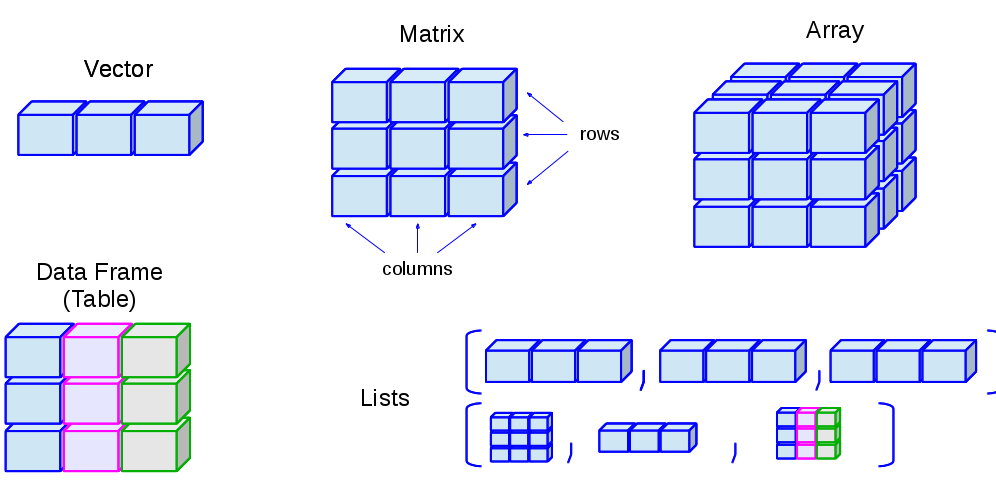
Base data structures of R can be classfied based on their dimension and type of data.
- Homogeneous means same type of data (e.g. number, character)
- Heterogeneous means different type of data (e.g. number and character)
| Dimension | Homogeneous | Heterogenous |
|---|---|---|
| 1-dim | Atomic Vector | List |
| 2-dim | Matrix | Data frame |
| n-dim | Array |
Exercise
How to know data strcture of your data
data(mtcars)
str(mtcars)
'data.frame': 32 obs. of 11 variables:
$ mpg : num 21 21 22.8 21.4 18.7 18.1 14.3 24.4 22.8 19.2 ...
$ cyl : num 6 6 4 6 8 6 8 4 4 6 ...
$ disp: num 160 160 108 258 360 ...
$ hp : num 110 110 93 110 175 105 245 62 95 123 ...
$ drat: num 3.9 3.9 3.85 3.08 3.15 2.76 3.21 3.69 3.92 3.92 ...
$ wt : num 2.62 2.88 2.32 3.21 3.44 ...
$ qsec: num 16.5 17 18.6 19.4 17 ...
$ vs : num 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 ...
$ am : num 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...
$ gear: num 4 4 4 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 ...
$ carb: num 4 4 1 1 2 1 4 2 2 4 ...
Vector
-
Vectors are the structures for dataset with 1-dimension.
-
Includes both Atomic vector and List
-
Homogenous data can be of the following type (logical, integer, double/numeric, and character)
-
When different datatypes are combined, types of data are converted.
-
The conversion follows the sequence character > double/numeric >logical
Vector
Let’s create one vector. c() creates vector in R programming.
vec <- c(1.2, 3,5, 8, 10.7)
vec
[1] 1.2 3.0 5.0 8.0 10.7
str(vec)
num [1:5] 1.2 3 5 8 10.7
length(vec)
[1] 5
Matrix and Array
Matrices are a special type of array with only two dimension.
mat <-matrix(1:10, nrow=5, ncol=2)
mat
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 1 6
[2,] 2 7
[3,] 3 8
[4,] 4 9
[5,] 5 10
str(mat)
int [1:5, 1:2] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
dim(mat)
[1] 5 2
Data frame
-
Most common way of storing data in R
-
Can store different types of data in same dataset
df <-data.frame(x = 1:3, y = c("a", "b", "d"))
df
x y
1 1 a
2 2 b
3 3 d
str(df)
'data.frame': 3 obs. of 2 variables:
$ x: int 1 2 3
$ y: Factor w/ 3 levels "a","b","d": 1 2 3
dim(df)
[1] 3 2
Data frame
df1 <-data.frame(x = 1:3, y = c("a", "b", "d"), stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
df1
x y
1 1 a
2 2 b
3 3 d
str(df1)
'data.frame': 3 obs. of 2 variables:
$ x: int 1 2 3
$ y: chr "a" "b" "d"
str(df)
'data.frame': 3 obs. of 2 variables:
$ x: int 1 2 3
$ y: Factor w/ 3 levels "a","b","d": 1 2 3
Data import
Data can be imported in R by various functions.
Use head to check the first six rows of data and tail to check last six rows of data.
dat <-read.csv("D:/Work/random.csv",header = T)
head(dat)
Species.name IUCN.status Max.body.size
1 Torrent Tyrannulet Least Concerned 11
2 Sharp-tailed Streamcreeper Least Concerned 11
3 Plumbeous water Redstart Least Concerned 13
4 Drab Water Tyrant Least Concerned 14
5 Little Forktail Least Concerned 14
6 Luzon Redstart Vulnerable 15
Estimated.extent.of.occurrence
1 4280000
2 12500000
3 10800000
4 5690000
5 6330000
6 95300
Exercise
-
What is the difference between dim(matrix) and dim(data.frame) ?
-
If data.frame is a superset of matrix and other data structures, why do we use these data structures?
Operators
There are four main types of operators in R.
- Arithmatic
- Logical
- Miscellaneous
- Relational
Arithmatic operators
The following are the major arithmatic operator in R.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| + | Addition |
| - | Subtraction |
| * | Multiplication |
| / | Division |
| ^ | Exponent |
| %% | Modulus |
Logical operators
The following are the major logical operator in R.
These are applicable only to vectors.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| & | Element wise And |
| l | Element wise Or |
| ! | Not |
Miscellaneous operators
These operators are used for multiple operations in R.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| <- | Assignment operator |
| : | Colon operator |
| %in% | Identifies if an element belongs to a vector |
| %*% | Multiplication of a vector with its transpose |
Relational operators
The following are the major relational operator in R.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| < | Less than |
| > | Greater than |
| <= | Less than or equal to |
| >= | Greater than or equal to |
| == | Equal to |
| != | Not equal to |
Resources
For further readings
- Advanced R by Hadley Wickham http://adv-r.had.co.nz/
- R for Everyone: Advanced Analytics and Graphics by Jared Lander https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/r-for-everyone/9780133257182/
Questions
Please mail to nilanjanchatterjee7@gmail.com

